IMPORTANT NOTICE: shorthand dockerhub tags are OUTDATED. Please use long tags with the correct Arch for your CPU architecture, i.e. avoid latest or 1.5.0 tags and use instead amd64-v1.5.0 for 64bit processors, arm32v7-v1.5.0 for ARM v7, and so on. See issue.
Join the slack community over at the gophers workspace. Our Channel is #subspace which can be used to ask general questions in regards to subspace where the community can assist where possible.
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
- WireGuard VPN Protocol
- The most modern and fastest VPN protocol.
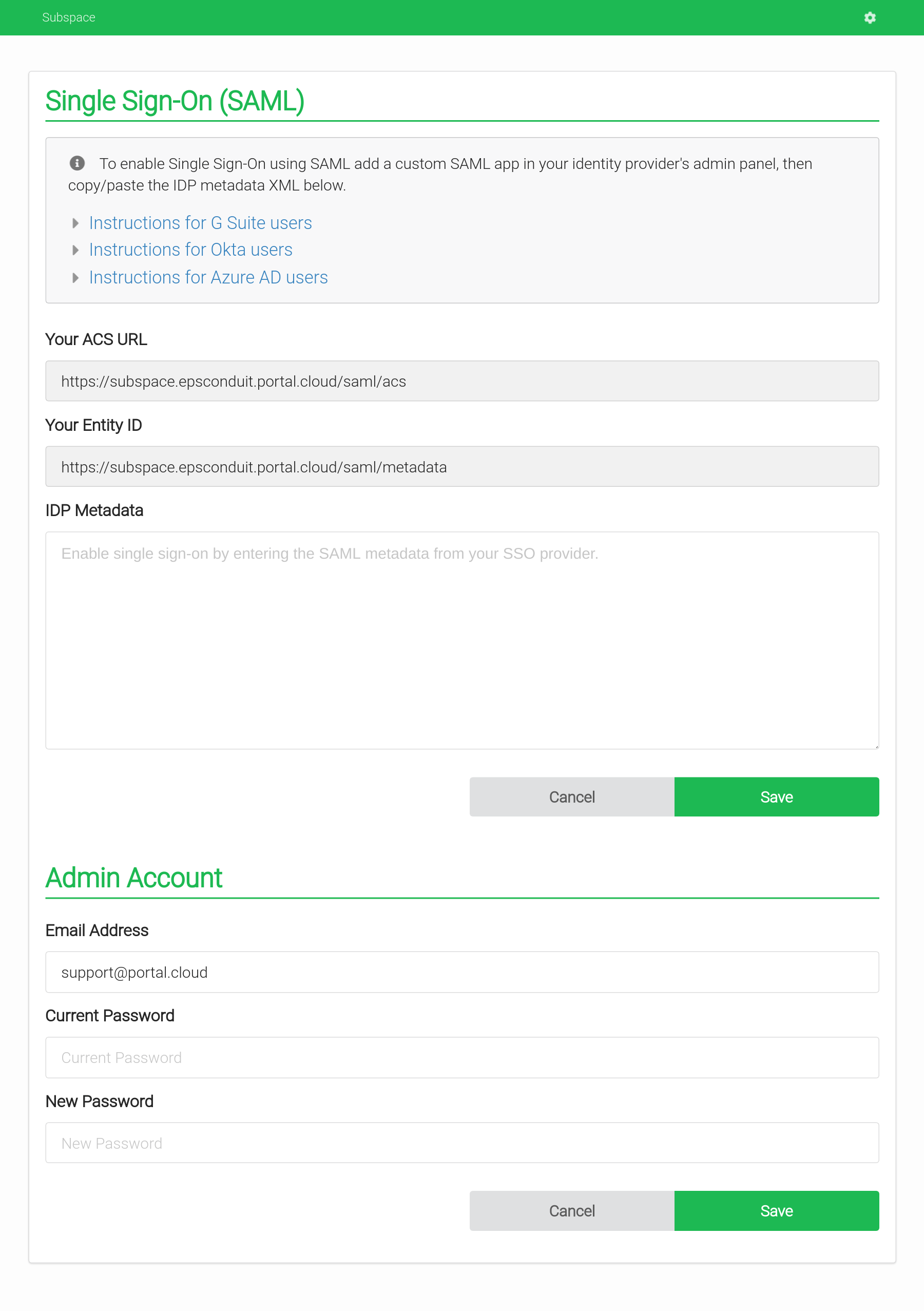
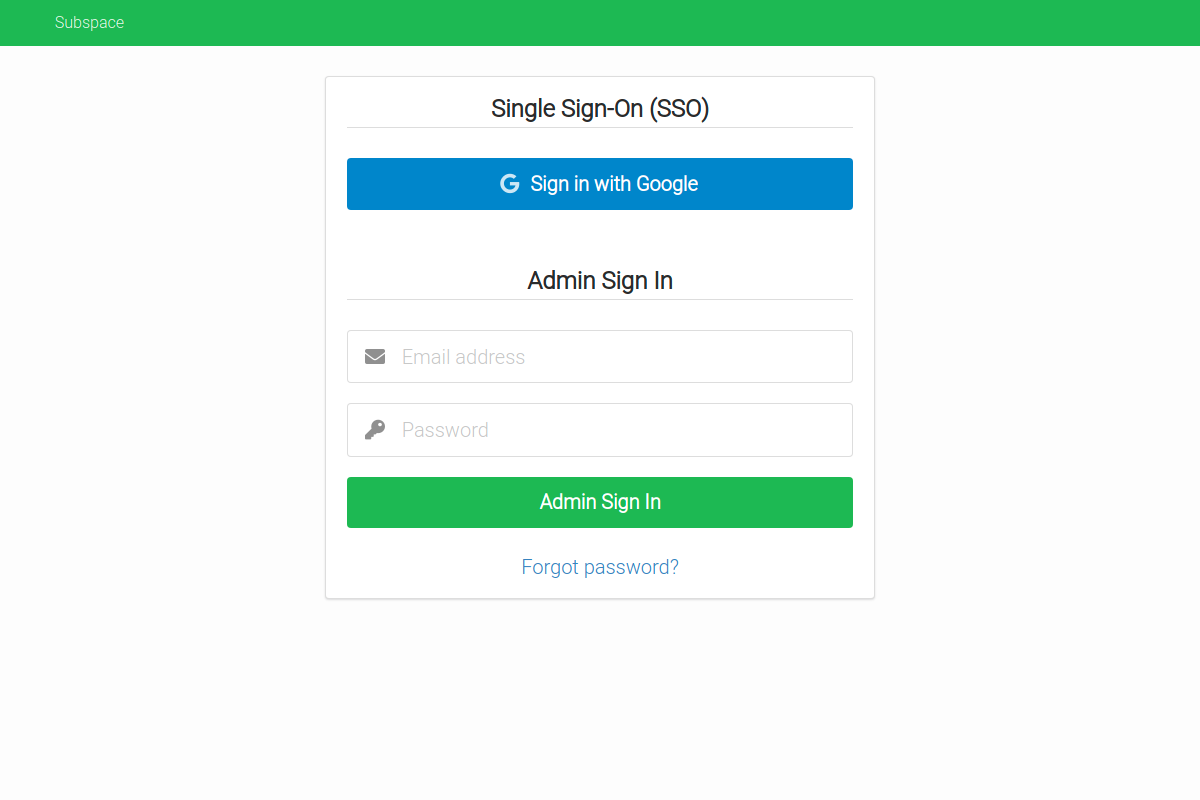
- Single Sign-On (SSO) with SAML
- Support for SAML providers like G Suite and Okta.
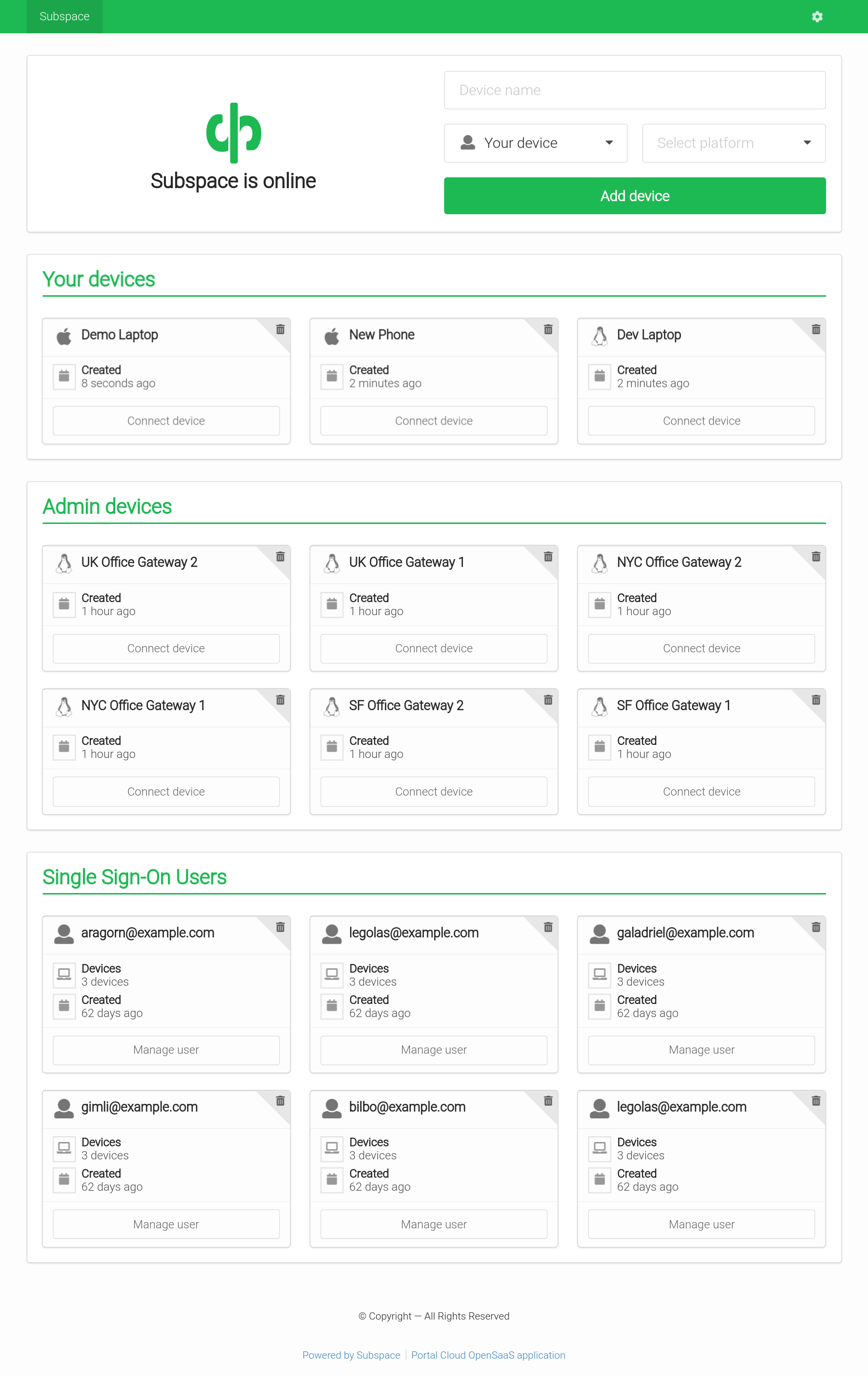
- Add Devices
- Connect from Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, Android, or iOS.
- Remove Devices
- Removes client key and disconnects client.
- Auto-generated Configs
- Each client gets a unique downloadable config file.
- Generates a QR code for easy importing on iOS and Android.
See the CONTRIBUTING page for additional info.
Recommended Specs
- Type: VPS or dedicated
- Distribution: Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial), 18.04 (Bionic) or 20.04 (Focal)
- Memory: 512MB or greater
Create a DNS A record in your domain pointing to your server's IP address.
Example: subspace.example.com A 172.16.1.1
Subspace runs a TLS ("SSL") https server on port 443/tcp. It also runs a standard web server on port 80/tcp to redirect clients to the secure server. Port 80/tcp is required for LetsEncrypt verification.
Requirements
- Your server must have a publicly resolvable DNS record.
- Your server must be reachable over the internet on ports 80/tcp, 443/tcp and 51820/udp (Default WireGuard port, user changeable).
Example usage:
$ subspace --http-host subspace.example.com| flag | default | description |
|---|---|---|
http-host |
REQUIRED: The host to listen on and set cookies for | |
backlink |
/ |
OPTIONAL: The page to set the home button to |
datadir |
/data |
OPTIONAL: The directory to store data such as the WireGuard configuration files |
debug |
OPTIONAL: Place subspace into debug mode for verbose log output | |
http-addr |
:80 |
OPTIONAL: HTTP listen address |
http-insecure |
OPTIONAL: enable session cookies for http and remove redirect to https | |
letsencrypt |
true |
OPTIONAL: Whether or not to use a LetsEncrypt certificate |
theme |
green |
OPTIONAL: The theme to use, please refer to semantic-ui for accepted colors |
version |
Display version of subspace and exit |
|
help |
Display help and exit |
| variable | default | description |
|---|---|---|
SUBSPACE_IPV4_POOL |
10.99.97.0/24 |
IPv4 Subnet to use as WireGuard subnet |
SUBSPACE_IPV6_POOL |
fd00::10:97:0/112 |
IPv6 Subnet to use as WireGuard subnet |
SUBSPACE_NAMESERVERS |
1.1.1.1,1.0.0.1 |
Nameservers to use, by-default those of Cloudflare. |
SUBSPACE_LETSENCRYPT |
1 |
Whether or not to use a LetsEncrypt certificate |
SUBSPACE_HTTP_ADDR |
:80 |
HTTP listen address |
SUBSPACE_HTTP_INSECURE |
false |
Enable session cookies for http and remove redirect to https |
SUBSPACE_LISTENPORT |
51820 |
Port for WireGuard to listen on |
SUBSPACE_ENDPOINT_HOST |
httpHost |
The host to listen on for the webserver, if it differs from the VPN GW. |
SUBSPACE_ALLOWED_IPS |
0.0.0.0/0, ::/0 |
Comma-separated list of IP's / subnets that are routed via WireGuard. By default everything is routed. |
SUBSPACE_IPV4_NAT_ENABLED |
true |
Whether to enable NAT routing for IPv4 |
SUBSPACE_IPV6_NAT_ENABLED |
true |
Whether to enable NAT routing for IPv6 |
SUBSPACE_THEME |
green |
The theme to use, please refer to semantic-ui for accepted colors |
SUBSPACE_BACKLINK |
/ |
The page to set the home button to |
SUBSPACE_DISABLE_DNS |
false |
Whether to disable DNS so the client uses their own configured DNS server(s). Consider disabling DNS server, if supporting international VPN clients |
SUBSPACE_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE |
0 |
Whether PersistentKeepalive should be enabled for clients (seconds) |
The container expects WireGuard to be installed on the host. The official image is subspacecommunity/subspace.
apt-get update
apt-get install -y wireguard
# Remove dnsmasq because it will run inside the container.
apt-get remove -y dnsmasq
# Disable systemd-resolved listener if it blocks port 53.
echo "DNSStubListener=no" >> /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
systemctl restart systemd-resolved
# Set Cloudfare DNS server.
echo nameserver 1.1.1.1 > /etc/resolv.conf
echo nameserver 1.0.0.1 >> /etc/resolv.conf
# Load modules.
modprobe wireguard
modprobe iptable_nat
modprobe ip6table_nat
# Enable modules when rebooting.
echo "wireguard" > /etc/modules-load.d/wireguard.conf
echo "iptable_nat" > /etc/modules-load.d/iptable_nat.conf
echo "ip6table_nat" > /etc/modules-load.d/ip6table_nat.conf
# Check if systemd-modules-load service is active.
systemctl status systemd-modules-load.service
# Enable IP forwarding.
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1
Follow the official Docker install instructions: Get Docker CE for Ubuntu
Make sure to change the --env SUBSPACE_HTTP_HOST to your publicly accessible domain name.
If you want to run the vpn on a different domain as the http host you can set --env SUBSPACE_ENDPOINT_HOST
Use --env SUBSPACE_DISABLE_DNS=1 to make subspace generate WireGuard configs without the DNS option, preserving the user's DNS servers.
# Your data directory should be bind-mounted as `/data` inside the container using the `--volume` flag.
$ mkdir /data
docker create \
--name subspace \
--restart always \
--network host \
--cap-add NET_ADMIN \
--volume /data:/data \
# Optional directory for mounting dnsmasq configurations
--volume /etc/dnsmasq.d:/etc/dnsmasq.d \
--env SUBSPACE_HTTP_HOST="subspace.example.com" \
# Optional variable to change upstream DNS provider
--env SUBSPACE_NAMESERVERS="1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8" \
# Optional variable to change WireGuard Listenport
--env SUBSPACE_LISTENPORT="51820" \
# Optional variables to change IPv4/v6 prefixes
--env SUBSPACE_IPV4_POOL="10.99.97.0/24" \
--env SUBSPACE_IPV6_POOL="fd00::10:97:0/64" \
# Optional variables to change IPv4/v6 Gateway
--env SUBSPACE_IPV4_GW="10.99.97.1" \
--env SUBSPACE_IPV6_GW="fd00::10:97:1" \
# Optional variable to enable or disable IPv6 NAT
--env SUBSPACE_IPV6_NAT_ENABLED=1 \
# Optional variable to disable DNS server. Enabled by default.
# consider disabling DNS server, if supporting international VPN clients
--env SUBSPACE_DISABLE_DNS=0 \
# Optional variable to change PersistentKeepalive
--env SUBSPACE_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE=20 \
subspacecommunity/subspace:latest
$ sudo docker start subspace
$ sudo docker logs subspace
<log output>
version: "3.3"
services:
subspace:
image: subspacecommunity/subspace:latest
container_name: subspace
volumes:
- /opt/docker/subspace:/data
- /opt/docker/dnsmasq:/etc/dnsmasq.d
restart: always
environment:
- SUBSPACE_HTTP_HOST=subspace.example.org
- SUBSPACE_LETSENCRYPT=true
- SUBSPACE_HTTP_INSECURE=false
- SUBSPACE_HTTP_ADDR=":80"
- SUBSPACE_NAMESERVERS=1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8
- SUBSPACE_LISTENPORT=51820
- SUBSPACE_IPV4_POOL=10.99.97.0/24
- SUBSPACE_IPV6_POOL=fd00::10:97:0/64
- SUBSPACE_IPV4_GW=10.99.97.1
- SUBSPACE_IPV6_GW=fd00::10:97:1
- SUBSPACE_IPV6_NAT_ENABLED=1
- SUBSPACE_DISABLE_DNS=0
- SUBSPACE_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE=20
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
network_mode: "host"
Pull the latest image, remove the container, and re-create the container as explained above.
# Pull the latest image
$ sudo docker pull subspacecommunity/subspace
# Stop the container
$ sudo docker stop subspace
# Remove the container (data is stored on the mounted volume)
$ sudo docker rm subspace
# Re-create and start the container
$ sudo docker create ... (see above)Thanks goes to these wonderful people (emoji key):
This project follows the all-contributors specification. Contributions of any kind welcome!


