Reliable messages for Moleculer services via external queue/channel/topic. Unlike moleculer built-in events, this is not a fire-and-forget solution. It's a persistent, durable and reliable message sending solution. The module uses an external message queue/streaming server that stores messages until they are successfully processed. It supports consumer groups, which means that you can run multiple instances of consumer services, incoming messages will be balanced between them.
- reliable messages with acknowledgement.
- multiple adapters (Redis, RabbitMQ, NATS JetStream, Kafka).
- plugable adapters.
- configurable max-in-flight.
- retry messages.
- dead-letter topic function.
- can receive messages from 3rd party services.
- graceful stopping with active message tracking.
npm i @moleculer/channels
Native Communication
Integration With A Third-Party System
Note: If you want to send messages to moleculer-services via channels from an external system, you must use the same serialization format as defined in the adapter options (default is
JSON). Otherwise, the services won't be able to parse the incoming messages.
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
logger: true,
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379"
})
]
};By default, the middleware will add a sendToChannel(<topic-name>, { payload }) method and channelAdapter property to the broker instance. Moreover, it will register handlers located in channels of a service schema.
module.exports = {
name: "payments",
actions: {
/*...*/
},
channels: {
// Shorthand format
// In this case the consumer group is the service full name
async "order.created"(payload) {
// Do something with the payload
// You should throw error if you want to NACK the message processing.
},
"payment.processed": {
// Using custom consumer-group
group: "other",
async handler(payload) {
// Do something with the payload
// You should throw error if you want to NACK the message processing.
}
}
},
methods: {
/*...*/
}
};The received
payloaddoesn't contain any Moleculer-specific data. It means you can use it to get messages from 3rd party topics/channels, as well.
broker.sendToChannel("order.created", {
id: 1234,
items: [
/*...*/
]
});The sent message doesn't contain any Moleculer-specific data. It means you can use it to produce messages to 3rd party topics/channels, as well.
Registering multiple adapters
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
// moleculer.config.js
module.exports = {
logger: true,
logLevel: "error",
middlewares: [
// Default options
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "Kafka",
options: {}
}
}),
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "Redis",
schemaProperty: "redisChannels",
sendMethodName: "sendToRedisChannel",
adapterPropertyName: "redisAdapter"
}),
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "AMQP",
schemaProperty: "amqpChannels",
sendMethodName: "sendToAMQPChannel",
adapterPropertyName: "amqpAdapter"
})
]
};Using multiple adapters in a service
module.exports = {
name: "payments",
actions: {
/*...*/
},
channels: {
"default.options.topic": {
group: "mygroup",
async handler(payload) {
/*...*/
}
}
},
redisChannels: {
"redis.topic": {
group: "mygroup",
async handler(payload) {
/*...*/
}
}
},
amqpChannels: {
"amqp.topic": {
group: "mygroup",
async handler(payload) {
/*...*/
}
}
}
};| Name | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
adapter |
String, Object |
null |
Adapter definition. It can be a String as name of the adapter or a connection string or an adapter definition Object. More info |
schemaProperty |
String |
"channels" |
Name of the property in service schema. |
sendMethodName |
String |
"sendToChannel" |
Name of the method in ServiceBroker to send message to the channels. |
adapterPropertyName |
String |
"channelAdapter" |
Name of the property in ServiceBroker to access the Adapter instance directly. |
context |
boolean |
false |
Using Moleculer context in channel handlers by default. |
Examples
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
logger: true,
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379",
sendMethodName: "sendToChannel",
adapterPropertyName: "channelAdapter",
schemaProperty: "channels"
})
]
};| Name | Type | Supported adapters | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
group |
String |
* | Group name. It's used as a consumer group in adapter. By default, it's the full name of service (with version) |
maxInFlight |
Number |
Redis | Max number of messages under processing at the same time. |
maxRetries |
Number |
* | Maximum number of retries before sending the message to dead-letter-queue or drop. |
deadLettering.enabled |
Boolean |
* | Enable "Dead-lettering" feature. |
deadLettering.queueName |
String |
* | Name of dead-letter queue. |
deadLettering.errorInfoTTL |
Number |
* | [Redis adapter only] TTL (in seconds) of error info messages stored in a separate hash. Default is 86400 (1 day). |
deadLettering.transformErrorToHeaders |
Function |
* | Function to parse error instance to a plain object which will be stored in message headers. |
deadLettering.transformHeadersToErrorData |
Function |
* | Function to parse plain error info object back to original data types |
context |
boolean |
* | Using Moleculer context in channel handlers. |
tracing |
Object |
* | Tracing options same as action tracing options. It works only with context: true. |
handler |
Function(payload: any, rawMessage: any) |
* | Channel handler function. It receives the payload at first parameter. The second parameter is a raw message which depends on the adapter. |
redis.startID |
String |
Redis | Starting point when consumers fetch data from the consumer group. By default equals to $, i.e., consumers will only see new elements arriving in the stream. More info here |
redis.minIdleTime |
Number |
Redis | Time (in milliseconds) after which pending messages are considered NACKed and should be claimed. Defaults to 1 hour. |
redis.claimInterval |
Number |
Redis | Interval (in milliseconds) between message claims |
redis.readTimeoutInterval |
Number |
Redis | Maximum time (in milliseconds) while waiting for new messages. By default equals to 0, i.e., never timeout. More info here |
redis.processingAttemptsInterval |
Number |
Redis | Interval (in milliseconds) between message transfer into FAILED_MESSAGES channel |
amqp.queueOptions |
Object |
AMQP | AMQP lib queue configuration. More info here. |
amqp.exchangeOptions |
Object |
AMQP | AMQP lib exchange configuration. More info here. |
amqp.consumerOptions |
Object |
AMQP | AMQP lib consume configuration. More info here. |
nats.consumerOptions |
Object |
NATS | NATS JetStream consumer configuration. More info here. |
nats.streamConfig |
Object |
NATS | NATS JetStream storage configuration. More info here. |
kafka.fromBeginning |
Boolean |
Kafka | Kafka consumer fromBeginning option. More info here. |
kafka.partitionsConsumedConcurrently |
Number |
Kafka | Kafka consumer partitionsConsumedConcurrently option. More info here. |
If the service is not able to process a message, it should throw an Error inside the handler function. In case of error and if maxRetries option is a positive number, the adapter will redeliver the message to one of all consumers. When the number of redelivering reaches the maxRetries, it will drop the message to avoid the 'retry-loop' effect. If the dead-lettering feature is enabled with deadLettering.enabled: true option then the adapter will move the message into the deadLettering.queueName queue/topic.
The dead-lettered message will contain the original payload and additional error information in the ctx.headers (for Moleculer version >= 0.15.x only) and in the raw message headers. Note that depending on the adapter, the raw message structure may differ (e.g, Map or Object, Buffer or String). The error information includes details about the original error that caused the message to be dead-lettered, such as the error message, stack trace, code, type, data, name, retryable status, and a timestamp indicating when the error occurred.
You can customize the error information that will be stored in the message headers by providing a custom transformErrorToHeaders function in the deadLettering options. By default, the parser stores the message, stack, code, type, data, name and retryable properties of the error object (if they exist) in the headers as plain string, except for stack and data properties which are stored as base64 encoded strings. Encoding is necessary to handle special characters, as some message brokers (like NATS JetStream) do not support characters like \n or \r in headers.
You can also provide a custom transformHeadersToErrorData function in the deadLettering options to parse the error information from the message headers back to their original data types when consuming dead-lettered messages in ctx.headers.
Also note that, for Redis adapter it's not possible to update the original message with error info, to overcome this limitation the adapter will store error info in a separate hash with the message ID as the key. You can customize the TTL of these error info message by setting deadLettering.errorInfoTTL, which defaults to 1 day. When Redis adapter moves a message to the dead-letter queue, it will merge the original message with the error info from the hash.
Default error to headers parser
/**
* Converts Error object to a plain object
* @param {any} err
* @returns {Record<string, string>|null}
*/
const transformErrorToHeaders = err => {
if (!err) return null;
let errorHeaders = {
// primitive properties
...(err.message ? { [HEADER_ERROR_MESSAGE]: err.message.toString() } : {}),
...(err.code ? { [HEADER_ERROR_CODE]: err.code.toString() } : {}),
...(err.type ? { [HEADER_ERROR_TYPE]: err.type.toString() } : {}),
...(err.name ? { [HEADER_ERROR_NAME]: err.name.toString() } : {}),
...(typeof err.retryable === "boolean"
? { [HEADER_ERROR_RETRYABLE]: err.retryable.toString() }
: {}),
// complex properties
// Encode to base64 because of special characters For example, NATS JetStream does not support \n or \r in headers
...(err.stack ? { [HEADER_ERROR_STACK]: toBase64(err.stack) } : {}),
...(err.data ? { [HEADER_ERROR_DATA]: toBase64(err.data) } : {})
};
if (Object.keys(errorHeaders).length === 0) return null;
errorHeaders[HEADER_ERROR_TIMESTAMP] = Date.now().toString();
return errorHeaders;
};Default headers to error info parser
/**
* Parses error info from headers and attempts to reconstruct original data types
*
* @param {Record<string, string>} headers
* @returns {Record<string, any>}
*/
const transformHeadersToErrorData = headers => {
if (!headers || typeof headers !== "object") return null;
const complexPropertiesList = [HEADER_ERROR_STACK, HEADER_ERROR_DATA];
let errorInfo = {};
for (let key in headers) {
if (!key.startsWith(HEADER_ERROR_PREFIX)) continue;
errorInfo[key] = complexPropertiesList.includes(key)
? parseBase64(headers[key])
: (errorInfo[key] = parseStringData(headers[key]));
}
return errorInfo;
};Dead-Letter Logic
The adapters track the messages that are being processed. This means that when a service or the broker is stopping the adapter will block the process and wait until all active messages are processed.
Use the broker.sendToChannel(channelName, payload, opts) method to send a message to a channel. The payload should be a serializable data.
| Name | Type | Supported adapters | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
raw |
Boolean |
* | If truthy, the payload won't be serialized. |
persistent |
Boolean |
AMQP | If truthy, the message will survive broker restarts provided it’s in a queue that also survives restarts. |
ttl |
Number |
AMQP | If supplied, the message will be discarded from a queue once it’s been there longer than the given number of milliseconds. |
priority |
Number |
AMQP | Priority of the message. |
correlationId |
String |
AMQP | Request identifier. |
headers |
Object |
AMQP, JetStream, Kafka, Redis | Application specific headers to be carried along with the message content. |
routingKey |
Object |
AMQP | The AMQP publish method's second argument. If you want to send the message into an external queue instead of exchange, set the channelName to "" and set the queue name to routingKey |
publishAssertExchange.enabled |
Boolean |
AMQP | Enable/disable calling once channel.assertExchange() before first publishing in new exchange by sendToChannel() |
publishAssertExchange.exchangeOptions |
Object |
AMQP | AMQP lib exchange configuration when publishAssertExchange enabled |
key |
String |
Kafka | Key of Kafka message. |
partition |
String |
Kafka | Partition of Kafka message. |
acks |
Number |
Kafka | Control the number of required acks. |
timeout |
Number |
Kafka | The time to await a response in ms. Default: 30000 |
compression |
any |
Kafka | Compression codec. Default: CompressionTypes.None |
xaddMaxLen |
Number or String |
Redis | Define MAXLEN for XADD command |
It is possible to wrap the handlers and the send method in Moleculer middleware. The module defines two hooks to cover it. The localChannel hook is similar to localAction but it wraps the channel handlers in service schema. The sendToChannel hook is similar to emit or broadcast but it wraps the broker.sendToChannel publisher method.
Example
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
const MyMiddleware = {
name: "MyMiddleware",
// Wrap the channel handlers
localChannel(next, chan) {
return async (msg, raw) => {
this.logger.info(kleur.magenta(` Before localChannel for '${chan.name}'`), msg);
await next(msg, raw);
this.logger.info(kleur.magenta(` After localChannel for '${chan.name}'`), msg);
};
},
// Wrap the `broker.sendToChannel` method
sendToChannel(next) {
return async (channelName, payload, opts) => {
this.logger.info(kleur.yellow(`Before sendToChannel for '${channelName}'`), payload);
await next(channelName, payload, opts);
this.logger.info(kleur.yellow(`After sendToChannel for '${channelName}'`), payload);
};
}
};
module.exports = {
logger: true,
middlewares: [
MyMiddleware,
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379"
})
]
};In order to use Moleculer Context in handlers (transferring ctx.meta and tracing information) you should set the context: true option in channel definition object or in middleware options to enable it for all channel handlers.
Example to enable context for all handlers
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
logger: true,
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379",
// Enable context in all channel handlers
context: true
})
]
};Using Context in handlers
module.exports = {
name: "payments",
actions: {
/*...*/
},
channels: {
"default.options.topic": {
context: true, // Unless not enabled it globally
async handler(ctx /*, raw*/) {
// The `ctx` is a regular Moleculer Context
if (ctx.meta.loggedInUser) {
// The `ctx.params` contains the original payload of the message
await ctx.call("some.action", ctx.params);
}
}
}
}
};Send message with parent Context
In this case the ctx.meta and other tracing information is transferred to the channel handler.
module.exports = {
name: "payments",
actions: {
submitOrder: {
async handler(ctx) {
await broker.sendToChannel(
"order.created",
{
id: 1234,
items: [
/*...*/
]
},
{
// Pass the `ctx` in options of `sendToChannel`
ctx
}
);
}
}
}
};To enable tracing for context-based handlers, you should register Tracing middleware in broker options.
The middleware works only with
context: true.
Register channel tracing middleware
//moleculer.config.js
const TracingMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Tracing;
module.exports = {
logger: true,
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379",
// Enable context in all channel handlers
context: true
}),
TracingMiddleware()
]
};You can fine-tuning tracing tags and span name in tracing channel property similar to actions.
Customize tags and span name
broker.createService({
name: "sub1",
channels: {
"my.topic": {
context: true,
tracing: {
spanName: ctx => `My custom span: ${ctx.params.id}`
tags: {
params: true,
meta: true
}
},
async handler(ctx, raw) {
// ...
}
}
}
});To disable tracing, set `tracing: false in channel definition.
| Name | Type | Default value | Supported adapters | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
consumerName |
String |
ServiceBroker nodeID | * | Consumer name used by adapters. By default it's the nodeID of ServiceBroker. |
prefix |
String |
ServiceBroker namespace | * | Prefix is used to separate topics between environments. By default, the prefix value is the namespace of the ServiceBroker. |
serializer |
String, Object, Serializer |
JSON |
* | Message serializer. You can use any built-in serializer of Moleculer or create a custom one. |
maxRetries |
Number |
3 |
* | Maximum number of retries before sending the message to dead-letter-queue or drop. |
maxInFlight |
Number |
1 |
* | Max number of messages under processing at the same time. |
deadLettering.enabled |
Boolean |
false |
* | Enable "Dead-lettering" feature. |
deadLettering.queueName |
String |
FAILED_MESSAGES |
* | Name of dead-letter queue. |
redis |
Object, String, Number |
null |
Redis | Redis connection options. More info here |
redis.consumerOptions .readTimeoutInterval |
Number |
0 |
Redis | Maximum time (in milliseconds) while waiting for new messages. By default equals to 0, i.e., never timeout. More info here |
redis.consumerOptions .minIdleTime |
Number |
60 * 60 * 1000 |
Redis | Time (in milliseconds) after which pending messages are considered NACKed and should be claimed. Defaults to 1 hour. |
redis.consumerOptions .claimInterval |
Number |
100 |
Redis | Interval (in milliseconds) between message claims. |
redis.consumerOptions .startID |
String |
$ |
Redis | Starting point when consumers fetch data from the consumer group. By default equals to $, i.e., consumers will only see new elements arriving in the stream. More info here. |
redis.consumerOptions .processingAttemptsInterval |
Number |
0 |
Redis | Interval (in milliseconds) between message transfer into FAILED_MESSAGES channel. |
redis.cluster |
Object |
null |
Redis | Redis cluster connection options. More info here |
redis.cluster.nodes |
Array |
null |
Redis | Redis Cluster nodes list. |
redis.cluster.clusterOptions |
Object |
null |
Redis | Redis Cluster options. |
amqp.url |
String |
null |
AMQP | Connection URI. |
amqp.socketOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib socket configuration. More info here. |
amqp.queueOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib queue configuration. More info here. |
amqp.exchangeOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib exchange configuration. More info here. |
amqp.messageOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib message configuration. More info here. |
amqp.consumerOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib consume configuration. More info here. |
amqp.publishAssertExchange.enabled |
Boolean |
false |
AMQP | Enable/disable calling once channel.assertExchange() before first publishing in new exchange by sendToChannel(). More info here. |
amqp.publishAssertExchange.exchangeOptions |
Object |
null |
AMQP | AMQP lib exchange configuration. More info here. |
nats.streamConfig |
Object |
null |
NATS | NATS JetStream storage configuration. More info here. |
nats.consumerOptions |
Object |
null |
NATS | NATS JetStream consumer configuration. More info here. |
kafka.brokers |
String[] |
null |
Kafka | Kafka bootstrap brokers. |
kafka.logCreator |
Function |
null |
Kafka | Kafka logCreator. More info here. |
kafka.producerOptions |
Object |
null |
Kafka | Kafka producer constructor configuration. More info here. |
kafka.consumerOptions |
Object |
null |
Kafka | Kafka consumer constructor configuration. More info here. |
Redis Streams was introduced in Redis 5.0. Hoverer, since this module relies on the XAUTOCLAIM command, Redis >= 6.2.0 is required.
To use this adapter, install the
ioredismodule with npm installiorediscommand.
Redis Adapter Overview
Example
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "redis://localhost:6379"
})
]
};Example with options
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "Redis",
options: {
redis: {
// ioredis constructor options: https://github.com/luin/ioredis#connect-to-redis
host: "127.0.0.1",
port: 6379,
db: 3,
password: "pass1234",
consumerOptions: {
// Timeout interval (in milliseconds) while waiting for new messages. By default never timeout
readTimeoutInterval: 0,
// Time (in milliseconds) after which pending messages are considered NACKed and should be claimed. Defaults to 1 hour.
minIdleTime: 5000,
// Interval (in milliseconds) between two claims
claimInterval: 100,
// "$" is a special ID. Consumers fetching data from the consumer group will only see new elements arriving in the stream.
// More info: https://redis.io/commands/XGROUP
startID: "$",
// Interval (in milliseconds) between message transfer into FAILED_MESSAGES channel
processingAttemptsInterval: 1000
}
}
}
}
})
]
};You can overwrite the default values in the handler definition.
Overwrite default options in service
module.exports = {
name: "payments",
actions: {
/*...*/
},
channels: {
"order.created": {
maxInFlight: 6,
async handler(payload) {
/*...*/
}
},
"payment.processed": {
redis: {
minIdleTime: 10,
claimInterval: 10
}
deadLettering: {
enabled: true,
queueName: "DEAD_LETTER"
},
async handler(payload) {
/*...*/
}
}
}
};Redis Cluster
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "Redis",
options: {
redis: {
cluster: {
nodes: [
{ port: 6380, host: "127.0.0.1" },
{ port: 6381, host: "127.0.0.1" },
{ port: 6382, host: "127.0.0.1" }
],
options: {
/* More information: https://github.com/luin/ioredis#cluster */
redisOptions: {
password: "fallback-password"
}
}
},
consumerOptions: {
// Timeout interval (in milliseconds) while waiting for new messages. By default never timeout
readTimeoutInterval: 0,
// Time (in milliseconds) after which pending messages are considered NACKed and should be claimed. Defaults to 1 hour.
minIdleTime: 5000,
// Interval (in milliseconds) between two claims
claimInterval: 100,
// "$" is a special ID. Consumers fetching data from the consumer group will only see new elements arriving in the stream.
// More info: https://redis.io/commands/XGROUP
startID: "$",
// Interval (in milliseconds) between message transfer into FAILED_MESSAGES channel
processingAttemptsInterval: 1000
}
},
deadLettering: {
transformErrorToHeaders: err => {
if (!err) return null;
let errorHeaders = {
// primitive properties
...(err.message
? { [HEADER_ERROR_MESSAGE]: err.message.toString() }
: {}),
...(err.code ? { [HEADER_ERROR_CODE]: err.code.toString() } : {}),
...(err.type ? { [HEADER_ERROR_TYPE]: err.type.toString() } : {}),
...(err.name ? { [HEADER_ERROR_NAME]: err.name.toString() } : {}),
...(typeof err.retryable === "boolean"
? { [HEADER_ERROR_RETRYABLE]: err.retryable.toString() }
: {}),
// complex properties
// Encode to base64 because of special characters For example, NATS JetStream does not support \n or \r in headers
...(err.stack ? { [HEADER_ERROR_STACK]: toBase64(err.stack) } : {}),
...(err.data ? { [HEADER_ERROR_DATA]: toBase64(err.data) } : {})
};
if (Object.keys(errorHeaders).length === 0) return null;
errorHeaders[HEADER_ERROR_TIMESTAMP] = Date.now().toString();
return errorHeaders;
},
transformHeadersToErrorData: headers => {
if (!headers || typeof headers !== "object") return null;
// parse back complex properties
const complexPropertiesList = [HEADER_ERROR_STACK, HEADER_ERROR_DATA];
let errorInfo = {};
for (let key in headers) {
if (!key.startsWith(HEADER_ERROR_PREFIX)) continue;
errorInfo[key] = complexPropertiesList.includes(key)
? parseBase64(headers[key])
: (errorInfo[key] = parseStringData(headers[key]));
}
return errorInfo;
},
// Time to live for error info in dedicated hash (in seconds). Default: 24 hours
errorInfoTTL: 24 * 60 * 60 // 24 hours
}
}
}
})
]
};To support Redis "capped streams", you can define the MAXLEN value in sendToChannel options as xaddMaxLen. It can be a number or a string with ~ prefix like ~1000. It will be transformed to ...MAXLEN ~ 1000 ...
Example
broker.sendToChannel(
"order.created",
{
id: 1234,
items: [
/*...*/
]
},
{
xaddMaxLen: "~1000"
}
);The AMQP adapter uses the exchange-queue logic of RabbitMQ for creating consumer groups. It means the sendToChannel method sends the message to the exchange and not for a queue.
To use this adapter, install the
amqplibmodule with npm installamqplibcommand.
Example
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "amqp://localhost:5672"
})
]
};Example with options
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "AMQP",
options: {
amqp: {
url: "amqp://localhost:5672",
// Options for `Amqplib.connect`
socketOptions: {},
// Options for `assertQueue()`
queueOptions: {},
// Options for `assertExchange()`
exchangeOptions: {},
// Options for `channel.publish()`
messageOptions: {},
// Options for `channel.consume()`
consumerOptions: {},
// Note: options for `channel.assertExchange()` before first publishing in new exchange
publishAssertExchange: {
// Enable/disable calling once `channel.assertExchange()` before first publishing in new exchange by `sendToChannel`
enabled: false,
// Options for `channel.assertExchange()` before publishing by `sendToChannel`
exchangeOptions: {}
}
},
maxInFlight: 10,
maxRetries: 3,
deadLettering: {
enabled: false
//queueName: "DEAD_LETTER",
//exchangeName: "DEAD_LETTER"
}
}
}
})
]
};Example Producing messages with options
broker.sendToChannel(
"order.created",
{
id: 1234,
items: [
/*...*/
]
},
{
// Using specific `assertExchange()` options only for the current sending case
publishAssertExchange: {
// Enable/disable calling once `channel.assertExchange()` before first publishing in new exchange by `sendToChannel`
enabled: true,
// Options for `channel.assertExchange()` before publishing
exchangeOptions: {
/*...*/
}
}
}
);Note: If you know that the exchange will be created before
sendToChannelis called by someone else, then it is better to skippublishAssertExchangeoption
The Kafka adapter uses Apache Kafka topics.
In Kafka adapter, the
maxInFlightfunction works differently than other adapters. Reading messages from a partition is processed sequentially in order. So if you want to process multiple messages, you should read messages from multiple partition. To enable it, use thekafka.partitionsConsumedConcurrentlyoption in channel options. More info.
To use this adapter, install the
kafkajsmodule with npm installkafkajscommand.
Example
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "kafka://localhost:9092"
})
]
};Example with options
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "Kafka",
options: {
kafka: {
brokers: ["kafka-1:9092", "kafka-1:9092"],
// Options for `producer()`
producerOptions: {},
// Options for `consumer()`
consumerOptions: {}
},
maxRetries: 3,
deadLettering: {
enabled: false,
queueName: "DEAD_LETTER"
}
}
}
})
]
};To use this adapter, install the
natsmodule with npm installnatscommand.
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "nats://localhost:4222"
})
]
};Example with options
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: {
type: "NATS",
options: {
nats: {
url: "nats://localhost:4222",
/** @type {ConnectionOptions} */
connectionOptions: {},
/** @type {StreamConfig} More info: https://docs.nats.io/jetstream/concepts/streams */
streamConfig: {},
/** @type {ConsumerOpts} More info: https://docs.nats.io/jetstream/concepts/consumers */
consumerOptions: {
config: {
// More info: https://docs.nats.io/jetstream/concepts/consumers#deliverpolicy-optstartseq-optstarttime
deliver_policy: "new",
// More info: https://docs.nats.io/jetstream/concepts/consumers#ackpolicy
ack_policy: "explicit",
// More info: https://docs.nats.io/jetstream/concepts/consumers#maxackpending
max_ack_pending: 1
}
}
},
maxInFlight: 10,
maxRetries: 3,
deadLettering: {
enabled: false,
queueName: "DEAD_LETTER"
}
}
}
})
]
};It is possible to configure single stream to handle multiple topics (e.g., streamOneTopic.abc and streamOneTopic.xyz). Moreover it possible for a single handler to receive any message that matches the filter streamOneTopic.*. Please check the example for all the details.
This adapter is made for unit/integration tests. The adapter uses the built-in Moleculer event bus to send messages instead of an external module. It means that the message sending is not reliable but can be a good option to test the channel handlers in a test environment. The fake adapter is doesn't support retries and dead-letter topic features. For multiple brokers, you should define a transporter (at least the FakeTransporter)
Do NOT use this adapter in production!
Example
// moleculer.config.js
const ChannelsMiddleware = require("@moleculer/channels").Middleware;
module.exports = {
middlewares: [
ChannelsMiddleware({
adapter: "Fake"
})
]
};Tests are running on Intel i7 4770K, 32GB RAM on Windows 10 with WSL.
| Name | Adapter | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Redis | Redis | Simple Redis Stream adapter. |
| RedisCluster | Redis | Clustered Redis Stream adapter with 3 nodes. |
| NATS JetStream | NATS | NATS JetStream adapter. |
| Kafka | Kafka | Kafka adapter. |
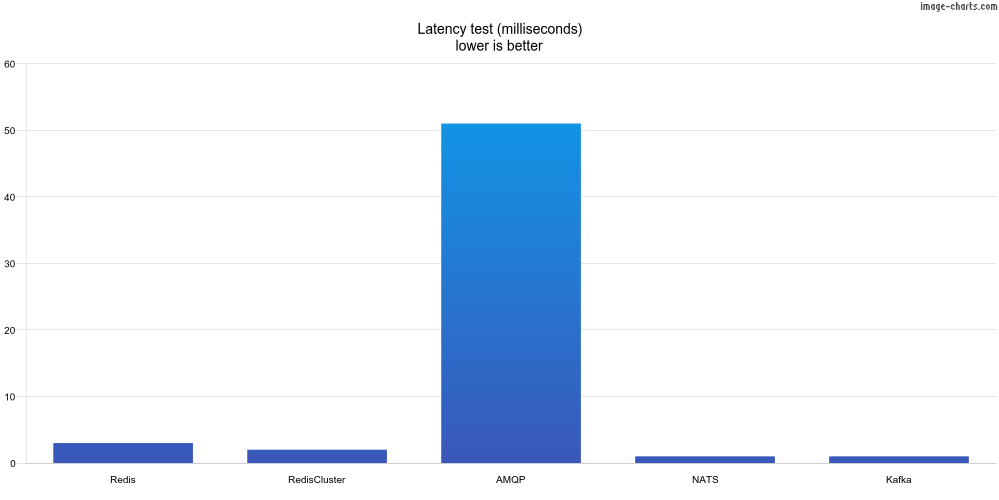
In this test, we send one message at a time. After processing the current message, another one is sent. This test measures the latency of processing a message. The maxInFlight is 1.
| Adapter | Time | msg/sec |
|---|---|---|
| Redis | 2ms | 452 |
| RedisCluster | 2ms | 433 |
| AMQP | 51ms | 20 |
| NATS JetStream | 1ms | 584 |
| Kafka | 1ms | 637 |
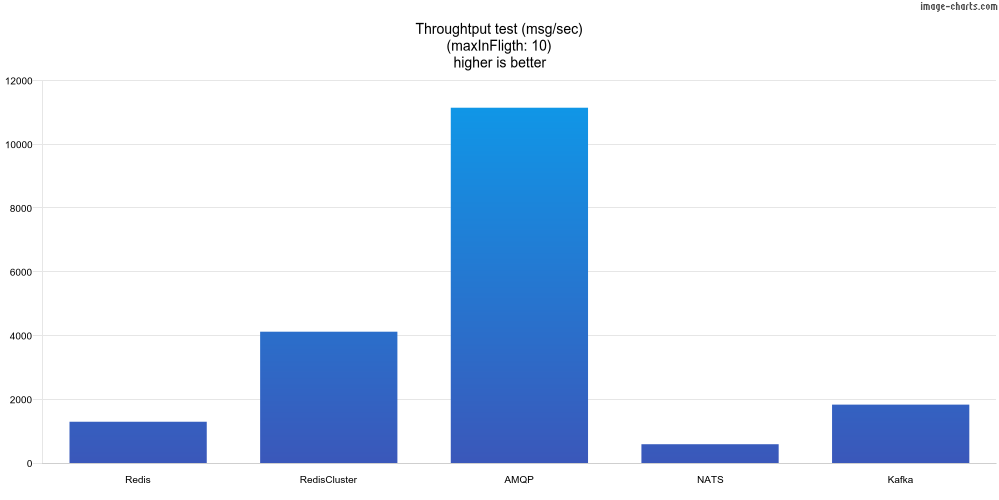
In this test, we send 10k messages and wait for all be processed. This test measures the throughput. The maxInFlight is 10.
| Adapter | msg/sec |
|---|---|
| Redis | 1294 |
| RedisCluster | 4118 |
| AMQP | 11143 |
| NATS JetStream | 589 |
| Kafka | 1831 |
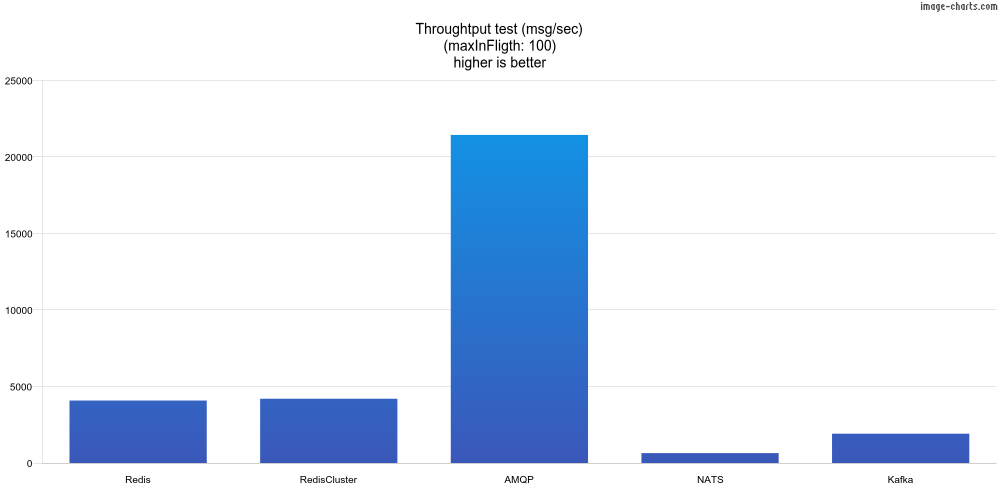
In this test, we send 10k messages and wait for all be processed. This test measures the throughput. The maxInFlight is 100.
| Adapter | msg/sec |
|---|---|
| Redis | 4081 |
| RedisCluster | 4198 |
| AMQP | 21438 |
| NATS JetStream | 646 |
| Kafka | 1916 |
The project is available under the MIT license.
Copyright (c) 2025 MoleculerJS