ROS-MCP-Server connects large language models (such as Claude, GPT, and Gemini) with existing robots giving them bidirectional AI integration.
With no changes to existing robot source code, this enables:
- 🗣 Commanding the robot in natural language → instructions are translated into ROS/ROS2 commands.
- 👀 Giving AI full visibility → subscribe to topics, call services, read sensor data, and monitor robot state in real time.
- No robot code changes → only requires adding the
rosbridgenode. - True two-way communication → LLMs can both control robots and observe everything happening in ROS (sensors, topics, parameters).
- ROS1 & ROS2 support → works with both versions out of the box.
- MCP-compatible → integrates with any MCP-enabled LLM (Claude Desktop, Gemini, ChatGPT, and beyond).
🖥️ Example - Controlling the MOCA mobile manipulator in NVIDIA Isaac Sim
Commands are entered into Claude Desktop, which uses the MCP server to directly drive the simulated robot.
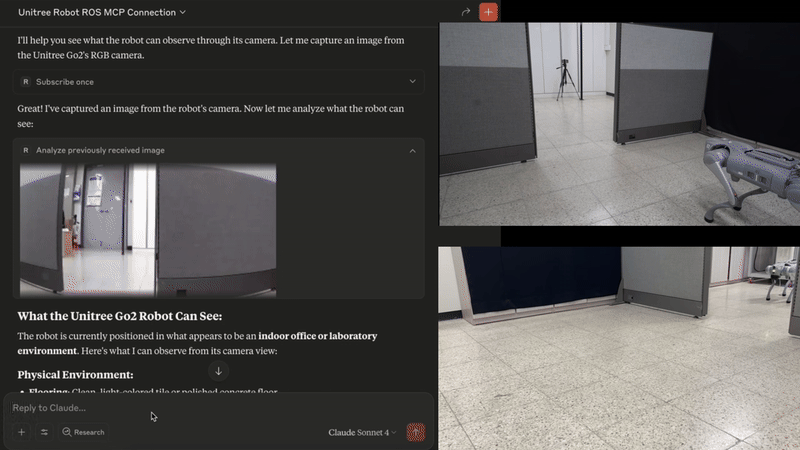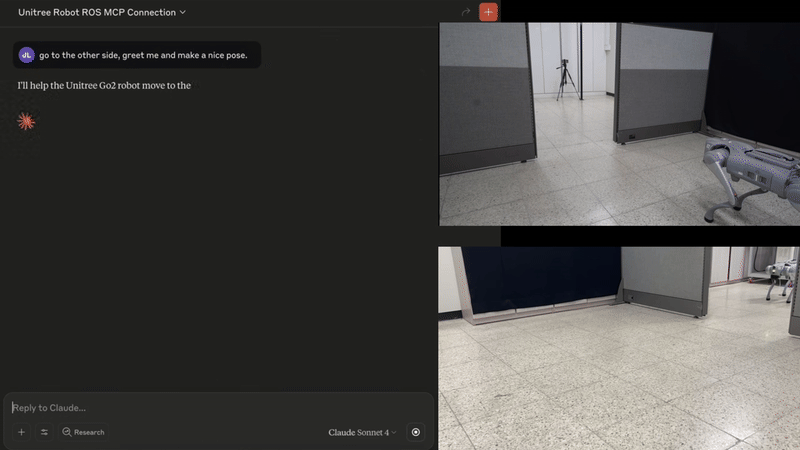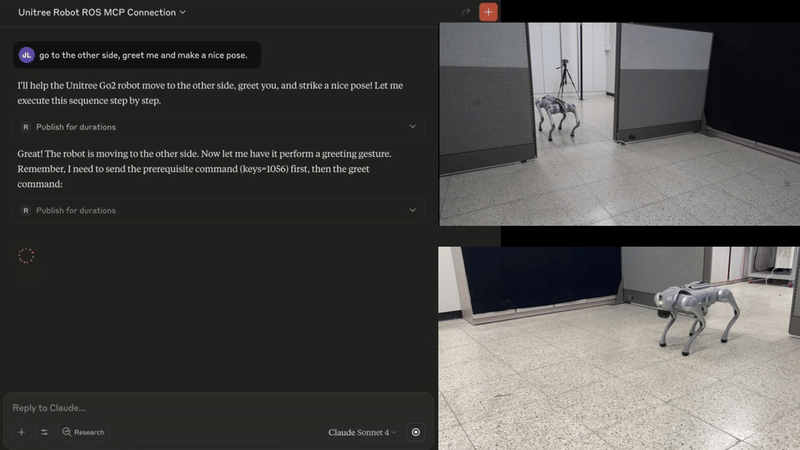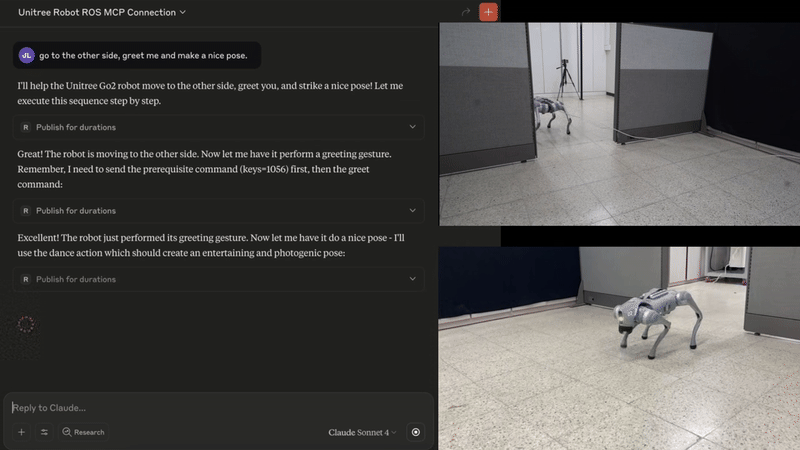
🐕 Example - Controlling Unitree Go with natural language (video)
The MCP server enables the Claude to interpret images from the robot's cameras, and then command the robot based on human natural language commands.
🏭 Example - Debugging an industrial robot (Video)
- Connecting to an industrial robot enables the LLM to browse all ROS topics and services to assess the robot state.
- With no predefined context, the MCP server enables the LLM to query details about custom topic and service types and their syntax (00:28).
- Using only natural language, the operator calls the custom services to test and debug the robot(01:42).
- List topics, services, and message types → explore everything available in your robot’s ROS environment.
- View type definitions (incl. custom) → understand the structure of any message.
- Publish/subscribe to topics → send commands or stream robot data in real time.
- Call services (incl. custom) → trigger robot functions directly.
- Get/set parameters → read or adjust robot settings on the fly.
- 🔜 Action support → upcoming support for ROS Actions.
- 🔜 Permission controls → manage access for safer deployments.
The MCP server is version-agnostic (ROS1 or ROS2) and works with any MCP-compatible LLM.
Follow the installation guide for step-by-step instructions:
- Clone the repository
- Install
uvandrosbridge - Install Claude Desktop (or any MCP-enabled client)
- Configure your client to connect to the ROS MCP Server
- Start
rosbridgeon the target robot
Browse our examples to see the server in action.
We welcome community PRs with new examples and integrations!
We love contributions of all kinds:
- Bug fixes and documentation updates
- New features (e.g., Action support, permissions)
- Additional examples and tutorials
Check out the contributing guidelines and see issues tagged good first issue to get started.
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.